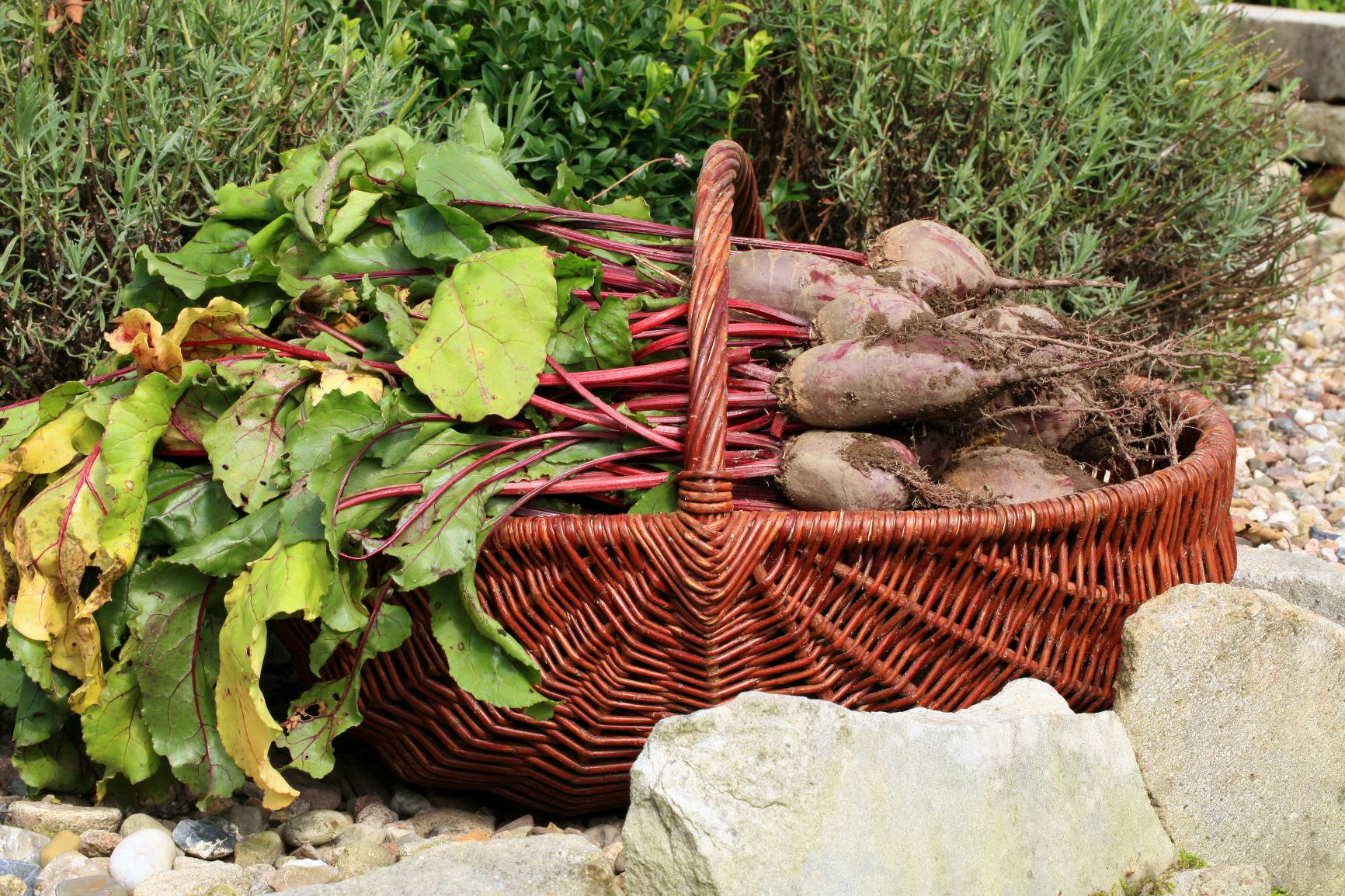

Harvesting, Storing & Preserving Beetroot
If stored and preserved correctly, beetroot can be kept all winter long and can enrich your diet. But when is the best time to harvest beetroot and what should you bear in mind when storing it? You can also find tips on how to preserve beetroot here.
This Article Contains:
Quick Overview
When to Harvest Beetroot?
- Beetroot is ready to harvest after 3 - 4 months in the bed, when they are about the size of a tennis ball
- Harvesting beetroot - here's how: Bundle the leaves and pull the beetroot out of the soil; loosen the soil with a digging fork if necessary
- Harvest time is from July until the first frosts, depending on the variety
Storing Beetroot - What You Need to Bear in Mind
- Remove leaves with a twisting motion before storage
- Only store undamaged beets
- Only roughly remove soil residues, do not wash!
- Store in wooden crates with damp sand or earth mounds
Preserving Beetroot
- There are many ways to preserve beetroot, such as preserving beetroot
- Are beet leaves edible? - Yes, they are edible and even very healthy. You can process the leaves like young spinach.
Harvesting Beetroot: How to Do It
Beetroot is ripe when the beets have reached about the size of a tennis ball and the leaves are blotchy. However, if the plants are left to grow for longer, the beetroots can become much larger. The small turnips taste particularly fine and aromatic. To harvest, simply bundle all the leaves and pull the beetroot out of the ground by it. For particularly deep varieties, you can carefully help from below with a digging fork. When harvesting, be careful not to damage the main root. If it is damaged, the red juice will leak out and the beet will "bleed to death". The damaged beets should be used as quickly as possible as they cannot be stored.
When to Harvest Beetroot?
Beetroot is harvested from July until shortly before the first frosts in October/November. The first beetroots are ready to harvest after 3 - 4 months, but they can also remain in the ground for longer. The harvest time depends on when the beetroot is sown. Early sowings from mid-April can be harvested and eaten fresh as early as July. For storage over the winter, it is best to sow beetroot in June and let the plants grow until shortly before the first frost. As the small beetroots are particularly tasty, it is a good idea to harvest individual plants over the course of the summer and leave a few to grow until the first frosts. Choose a storable variety for late cultivation, e.g. the "Rote Kugel". This variety "Jannis", for example, is very suitable for eating raw.
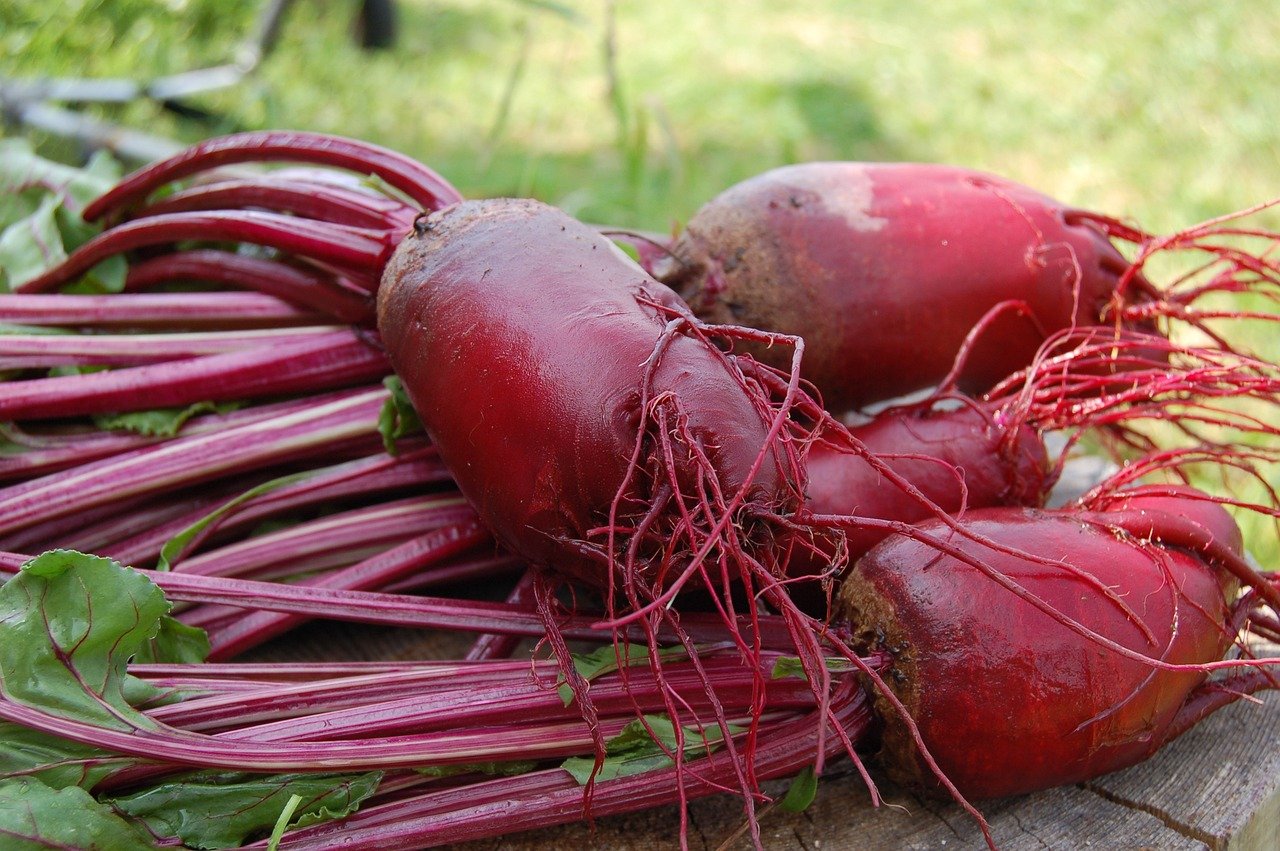

Storing Beetroot
Before storing, the leaves are removed with a twisting motion or cut off 2 cm/0.8 in above the beetroot. They are easy to remove and the heart of the beet remains undamaged. If, on the other hand, the beetroot is damaged, the deep red juice leaks out and it "bleeds to death". Make sure you only store undamaged beetroot, otherwise pathogens can penetrate the beetroot through open areas and cause it to rot. Do not wash the beetroot before storing, but only roughly remove the soil residues.
To store your supplies over the winter, layer the beets in wooden crates with damp sand so that they do not touch each other. Then place the crate in a cool, dark place with high humidity. An unheated cellar with temperatures of around 3 - 4 °C/37.4 - 39.02 °F is ideal. Under these conditions, the beetroot will not dry out so easily and will keep until spring. Individual beetroots can then be taken out of the box and used as required.
You Want to Know More About Beetroots?
In our library you will find information on the individual varieties with cultivation periods, tips on planting and harvesting. You will also find companion plants to help you plan a mixed crop.
View Library NowProcessing Beetroot Correctly
Beetroots can be used in a variety of ways. As a raw vegetable salad, it is often combined with apples. But beetroots also makes a great addition to tomato soup! The earthy taste complements the fresh sweetness of the tomato perfectly. Dark red varieties also give the soup an incomparably strong color. With horseradish, beetroots makes a deliciously spicy spread. You can experiment with different flavors when processing beetroot. This always results in unexpected combinations that are always delicious and healthy!
Are Beetroot Leaves Edible?
What many people don't know: The leaves are also edible. You can cook them in a similar way to spinach or use the young leaves as a baby leaf salad. They taste mildly nutty and are nice and crunchy. If you have large quantities, you can also turn them into pesto. Simply mix the chopped leaves with roasted pine nuts, parmesan, garlic, olive oil and a little lemon juice. Puree, season with salt and pepper and you're done!

Preserving Beetroot
You can Preserve the Compact Beetroot Using Fermentation or Other Methods for example. Beetroot can be preserved very well in vinegar. You can also freeze them in portions, cut into small pieces and cooked.
Boil the Beetroot
You can also easily boil down beetroot to preserve it. To do this, first boil the whole beetroots for around 45 minutes until they are cooked. Then peel them and cut them into slices. A little tip on the side: if you rinse the turnips with cold water after cooking, they are easier to peel. Now make a stock of vinegar, salt and sugar and leave the beetroot slices in it overnight. For two kilograms of beetroot (cooked and peeled), you will need around 300 ml/0.63 pt of vinegar, as well as a tablespoon of salt and two tablespoons of sugar. Once everything is well infused, pour the beet and the stock into boiled jars and seal well. If you like, you can add a quarter of an onion, a bay leaf and cloves to each jar. Then boil the jars in a preserving pot at 80 °C/176 °F for 30 minutes. If you don't have a preserving pot, you can use a normal large pot and bring the water to a gentle simmer. Make sure that the jars in the pot are completely covered with water.
Obtaining Your Own Beetroot Seeds: Here’s How
Beetroot cannot pollinate itself, it is mainly pollinated by the wind. When flowering at the same time, different members of the Chenopodiaceae can therefore cross-pollinate with each other. If you want to obtain seed from a particular variety, you should only allow this variety to flower. You can then either cut off the other inflorescences or prevent wind pollination by growing them under fleece.
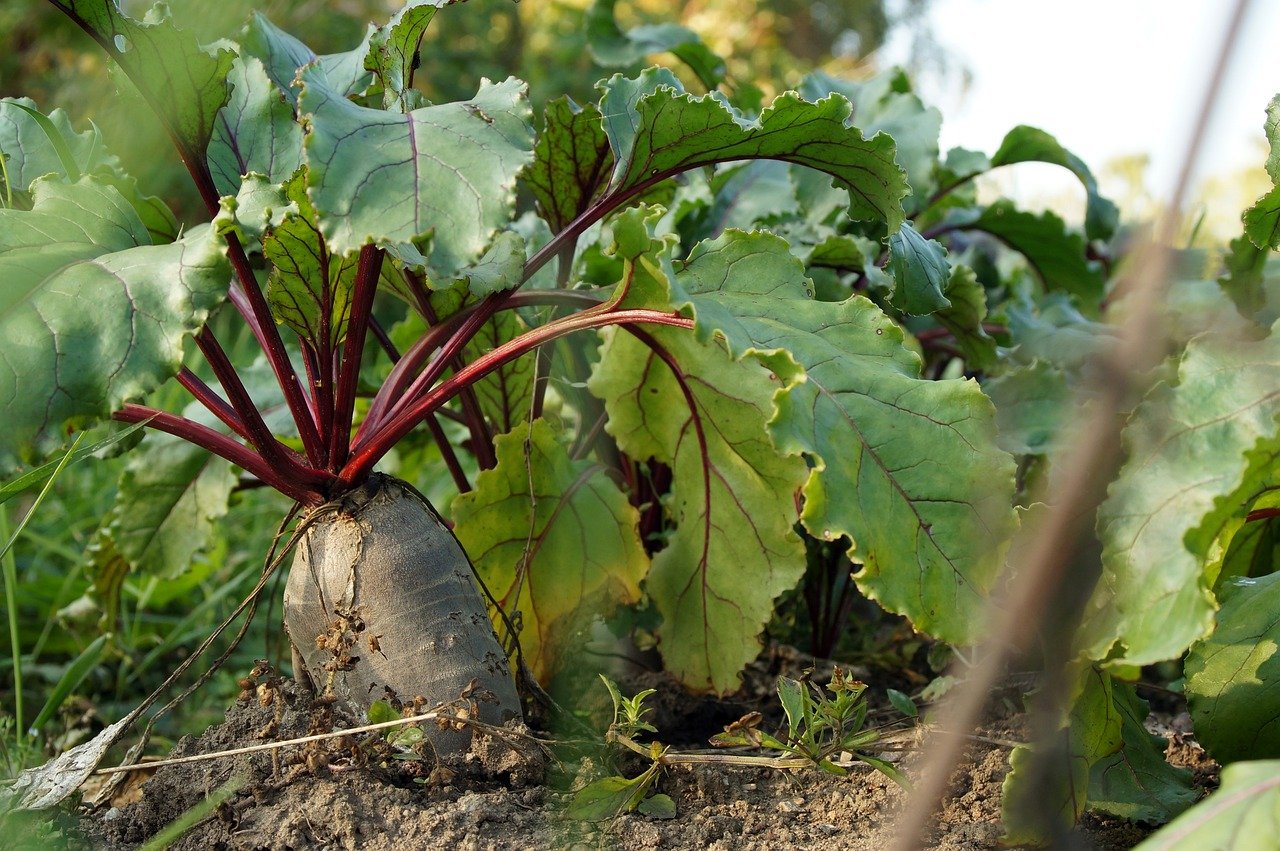

1) Bring In After the First Year for Overwintering
In the fall before the first frosts, select the strongest and healthiest plants. Remove the leaves 2 - 3 cm/0.8 - 1.2 in above the beetroot. Plant the seed carriers in wooden boxes with a mixture of soil and wood shavings. Keep the boxes moist but not too wet over the winter and store them in a frost-free cellar. At temperatures below - 41 °C, the beets would otherwise develop fine cracks, making them susceptible to rot.
2) Plant Out Again in the Second Year
From mid-March, you can then plant out the overwintered beetroot plants at a distance of 50 x 50 cm/19.7 x 19.7 cm. Cover the beetroot completely with soil and water well. It can be useful to support the inflorescences with a bamboo stick or similar, as they can grow up to 1.5 m/1.6 yd high. The flowers exude a wonderfully sweet fragrance.
3) Seed Harvest
You can usually start harvesting the seeds at the end of August, as soon as about 2/3 of the seeds have turned brown. Simply strip the seeds carefully with your fingers and collect them in a bowl. You can repeat this process over the next four weeks until all the seeds are ripe. After harvesting, dry the seeds again, put them in a paper bag and label them with the variety and year. If stored in a cool, dry place, the seeds will keep for at least four years.
If you have any questions or comments, please write to us at [email protected].
Would you like to receive helpful gardening tips all year round and plan your own beds optimally? Then register here or download the Fryd app for Android or iOS.
Fryd - Your digital bed planner

Marie
Marie is an agronomist. She is particularly interested in the sustainable and organic cultivation of vegetables and other plants. In her own garden, she gained experience and likes to try things out to learn from nature. She is particularly interested in the values and principles of permaculture, in order to contribute not only to the well-being of nature, but also to the well-being of people and future generations.
Learn MoreCurrent Topics in the Community
What would you recommend for my first year of raised bed gardening? Larger plants (tomatoes and cucumbers) will go in the greenhouse. #raisedbed #firstyearraisedbed #beginnersraisedbed
Show 2 answers# clay irrigation 2026 I would like to install clay irrigation systems on the left and right sides of the path in my polytunnel. Unfortunately, I can't upload the picture... I have no idea what I've been doing wrong since the update.
Show 2 answers
Liked 1 times
My Prunus Persica...always a dream😍
Popular Articles

Gardening in March: Preparation & Cultivation

Propagating Peppers/Chillies: How to Grow Them Successfully

Cultivation or Direct Sowing: When and Which Vegetables to Propagate?

Sowing and Propagating Tomatoes: This Is How It Works

Raised Beds: Your Planting Plan for a Year

Plant Lights for Growing and Overwintering Plants

Growing Cucumbers Seedlings in Pots: Tips for Propagation

Pricking Out Vegetable Plants: Tips and Instructions

Growing & Harvesting Rocket: Good & Bad Companion Plants

How to Grow Broccoli: Tips for Cultivation
FAQ
When is the best time to harvest beets?
Beets can be harvested from July until the first frosts, ideally when they reach the size of a tennis ball.
How should beetroots be stored?
Remove the leaves by twisting them off and store the undamaged beets. The best method is to store them in wooden boxes with moist sand in a cool, dark place.
Yes, the leaves are edible and very healthy. They can be prepared like spinach or used as baby leaf salad.
Beets can be preserved by canning, fermenting, or freezing. For canning, cook the beets, peel them, slice them, and place them in a brine made of vinegar, salt, and sugar.
How to obtain your own beet seeds?
Choose strong plants, overwinter them in a frost-free place, and replant them in spring. The seeds can be harvested from August when they turn brown.