
Lime Fertilizer: Tips for Properly Liming Garden Soil
Over time and with increasing age, most garden soils acidify. To counteract this, gardeners regularly apply lime to their soil. Lime is a soil additive that rejuvenates the soil, promotes soil processes and thus improves the soil structure. In addition, the mineral calcium contained in lime is an important nutrient for plants and strengthens plant immunity. Read this article to find out how to apply lime fertilizer in the garden and what you need to bear in mind!
This Article Contains:
Quick Overview
Lime Fertilizer: Uses in the Garden
- How to recognize lime deficiency:
- Soil is encrusted, low humus content, low pH value, acid-loving indicator plants like sorrel, speedwell or farmer's mustard
- Plants show symtoms such as chlorosis on young leaves and shoot tips
- Choose the right lime fertilizer:
- Garden lime for light to medium-heavy soils
- Calcareous marl is particularly suitable for sandy soil
- Algae lime is good for humus-rich garden soil and most likely foliar applicated
What Is Lime?
Lime mainly contains calcium, in different chemical forms depending on the lime fertilizer. Some limes also contain other nutrients and trace elements. Lime occurs naturally in many types of rock as calcium carbonate (carbonated lime) and is released in the soil through weathering. Therefore, lime, like all other nutrients, is used up and must be replaced. If no lime is added, your garden soil will acidify over time.

Why Lime the Garden at All?
Garden Soil Acidifies Over Time
As soil ages, it is quite natural that the soil acidifies over time and the pH value drops. There are numerous reasons for this: in addition to natural acid inputs from plants or rain, gardeners also contribute to soil acidification through fertilizers, for example.
Our tip: Nitrogen fertilizers contain either nitrate or ammonium. Both fertilizers have an effect on the pH value in the soil. Nitrate has an alkaline effect, i.e. raises the pH value. Ammonium contributes to soil acidification as it lowers the soil pH. So if it is necessary to fertilize your plants with nitrogen-containing liquid fertilizer, use fertilizer with nitrate to prevent soil acidification.
Lime Is Important for Soil and Plants
Lime can be used to improve acidic and nutrient-poor Garden Soils. Nutrients, especially phosphorus, are not available to plants in an excessively acidic environment. This can lead to deficiency symptoms and poor growth. In addition, biological activity is lower, which slows down soil processes.
You should therefore regularly measure the pH value in your garden and lime if necessary to bring the pH value into an optimum range and keep it there. Nutrients are then most readily available to plants and fertilizers can be efficiently absorbed by the plants, which reduces environmentally harmful nutrient leaching. Biological activity is also boosted, humus is built up and the soil structure is improved. This reduces the risk of silting and erosion.

Recognizing Lime Deficiency in the Garden
Lime Deficiency in the Soil: Improve Acidic Garden Soil
- Recognize lime deficiency: Encrusted garden soil; low humus content; no loose crumb structure; pH value less than 6, acid-loving indicator plants
- Carry out a pH measurement: there are tests you can carry out yourself or laboratories that will do this for you (contact points would be pharmacies, gardening associations or chambers of agriculture)
- Important: pH measurement is only a rough guide. The actual acidity is actually higher, depending on the type of soil. Soils have a natural buffering effect against acidity, which varies depending on the type of soil. Clay soil buffers the most acidity, whereas sandy soil buffers the least.
- The optimum pH value therefore also varies depending on the type of soil. You should know the type of soil in your garden before applying lime fertilizer in order to choose the right lime fertilizer.
| Soil Type | Optimal pH Range |
|---|---|
| Clay | 6,5 - 7 |
| Sandy loam | 6,0 |
| Sand | not under 5,5 |
Acid-Loving Indicator Plants
- farmer's mustard
- hare clover
- speedwell
- dog's chamomile
- sorrel
- mosses
- pansy
- field horsetail
- bilberry
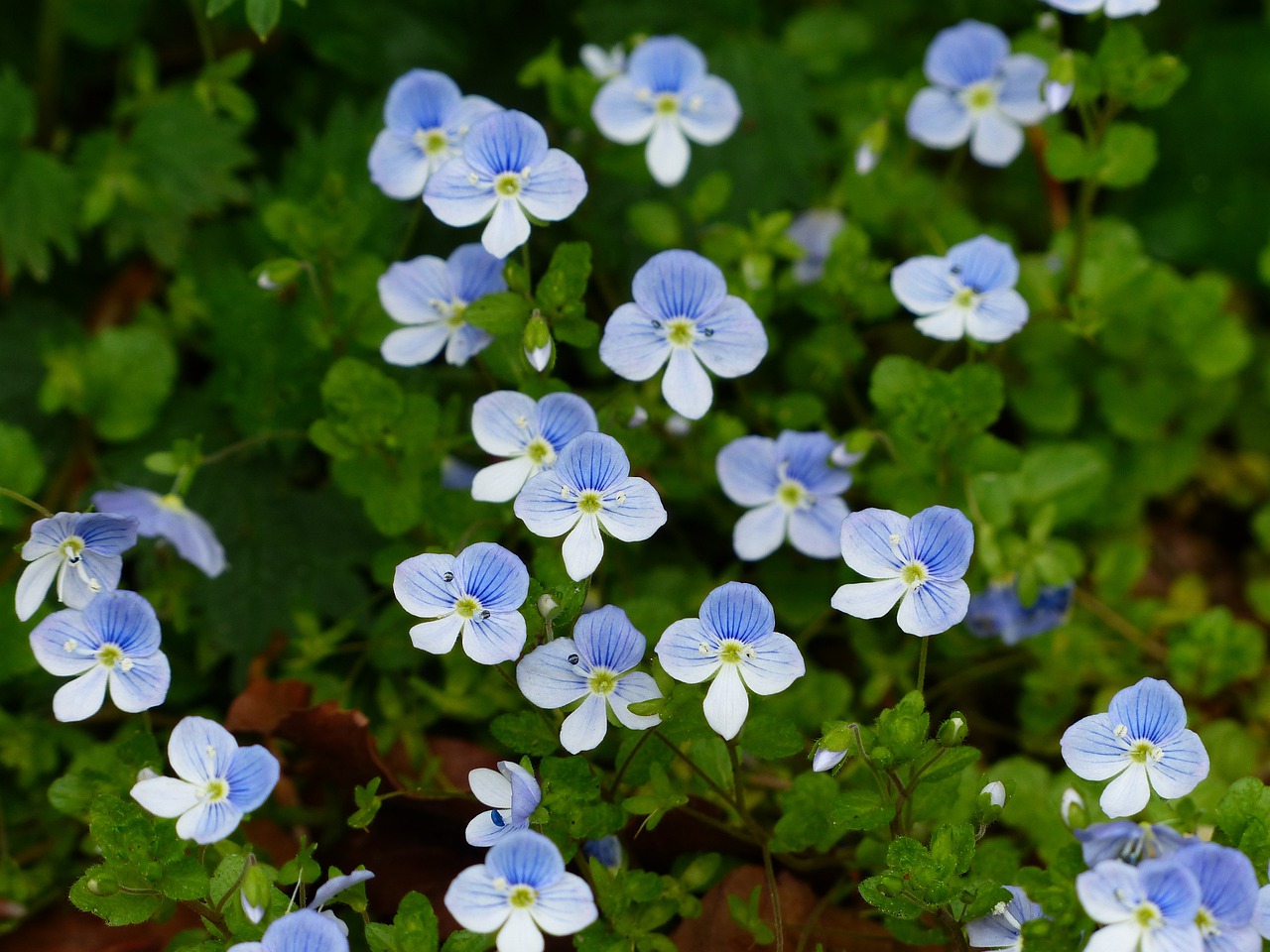

Lime Deficiency in Plants
- Deficiency symptoms such as chlorosis on young leaves and shoot tips
- In tomatoes, calcium deficiency often leads to blossom end rot
- In fruit such as quinces and apples, the fruit develops small brown spots on the skin and in the flesh (also known as stippling)
- At a pH of less than 4.5, aluminum salts dissolve, which have a highly toxic effect on plants. The growth of most cultivated plants is restricted by aluminum. The leaves turn yellow and die. The roots are damaged and their growth is impaired. In such an acidic environment, the plant also suffers from other nutrient deficiencies, as many nutrients are not available to the plant.
You Need Further Assistance?
To exchange ideas with other gardeners and benefit from their experiences, you can visit our Fryd community. Perhaps someone has already limed their garden and can give you some tips.
Join Community NowLime Fertilizer for the Garden: Algae Lime, Garden Lime & Co
Lime fertilizers such as garden lime, lime marl, algae lime and Rock Flour with mainly carbonated lime are well suited for the hobby garden. These lime fertilizers contain a lot of natural lime, which works gently and slowly in the soil, improving it in the long term. This is because these limes must first be broken down microbially before the nutrients become available to the plants and can take effect.
The soil is thus "fed" and builds up humus. This is good at first, but too much lime can leach out the soil in the long term. Too much biological activity can also lead to humus depletion and thus a decrease in soil fertility. You should therefore use lime with caution and always keep an eye on the soil pH.
In addition to the limes already listed, there are also quicklimes and slaked limes. These are fast-acting limes that react very aggressively in the soil and can even damage soil life in some cases. These limes are not suitable for hobby gardening and should therefore not be used.
Apply Lime as Fertilizer: Choose the Right Lime Fertilizer
Depending on the composition of your garden soil, there is a suitable lime fertilizer. In addition to classic limes such as garden lime, algae lime and marl lime, there are also rock powders. The effect and application of rock flours varies greatly, as they have an alkaline or acidic effect on the soil depending on the source rock. You can find out which rock flours are available and how to use them in the garden in our article on the subject.
| Lime Fertilizer | Application |
|---|---|
| Garden lime | light to medium-heavy soils |
| Calcareous marl | particularly suitable for sandy soils (due to clay content!) |
| Algae lime | humus-rich garden soil; foliar application to strengthen the plant |
The aim is to keep the soil pH in your garden as constant as possible over the years. As most garden soils acidify over the years, you should lime regularly. In this way, you replace the lime that has been used by the soil and plants and partly washed out. This is called maintenance liming.

Maintenance Liming as Soil Care
- When is the best time? Fall or spring is the best time. Carbonated limes act slowly. They have to dissolve in water and weather. It is therefore good to apply the lime in the fall before a damp period of rain and snow; alternatively in the spring
- How much lime? Every three years between 100 - 150 g per m2/3.5 - 5.3 fl. oz. per 1.2 yd2, depending on the type of soil
- How to apply lime? Apply to dry soil; do not inhale lime; work in well and water if necessary; do not sprinkle directly on plant parts as it can cause burns
- Clay soils need much more lime than sandy soils due to their high buffering capacity (the exact dosage is usually stated on the packaging)
- For clay soils, possibly spread two applications over the course of a year
- For sandy soils, lime or rock flour with clay content (e.g. lime marl) to improve the nutrient and water retention capacity
- Carry out maintenance liming on garden soil, vegetable beds and lawns
- Liming lawns: mow, verticalize and spread lime by hand
- Liming vegetablebeds: before or after the growing season
- Lime and fertilizer: always leave 2 or better 3 weeks between liming and fertilizing; otherwise the effect of fertilizers containing nitrogen in particular will be weakened
Improve Garden Soil: Adjust Soil PH
- Garden soil that is too acidic: Raise soil pH with liming; about 200 to 250 g per m2/7 to 8.8 fl. oz. per 1.2 yd2; avoid ammonium-containing fertilizers such as liquid manure
- Garden soil that is too calcareous: use basalt and granite rock flour to lower the pH; use nitrate-containing fertilizers
Indicator Plants for Alkaline Soil
- field campion
- meadow knapweed
- stinging nettle
- gallant
- sow thistle
- adonis roses
- dandelion
- dead nettle
- cranesbill

Lime to Strengthen Plants Against Pests and Diseases
- Naturally Strengthen Plants: Rock powders and algae lime in particular are also suitable for strengthening your plants' defenses. The powder is dusted onto the plant parts, which protects them from sucking pests and fungal diseases in particular. The fine dust wets the surface of the plants and thus prevents pathogens from settling.
- Caution: Insects are injured by the powder and can no longer move or breathe properly. Unfortunately, this affects all garden dwellers, which is why you should not apply lime or rock dust to your plants carelessly. Do not spray during the bee flight season or in areas in your garden where many insects live.
- You can find more Tips on Using Lime Such as Rock Flour Against Diseases and Pests in the article.
We hope all your questions about liming the garden have been answered. If you still have any questions or comments, please write to us at [email protected].
Would you like to receive helpful gardening tips all year round and plan your own beds optimally? Then register here or download the Fryd app for Android or iOS.
Fryd - your digital bed planner
Cover picture by Dr. Eugen Lehle on WikimediaCommons.

Marie
Marie is an agronomist. She is particularly interested in the sustainable and organic cultivation of vegetables and other plants. In her own garden, she gained experience and likes to try things out to learn from nature. She is particularly interested in the values and principles of permaculture, in order to contribute not only to the well-being of nature, but also to the well-being of people and future generations.
Learn MoreCurrent Topics in the Community

Liked 1 times
Finally, our clay soil has dried out a little and the spinach seeds from 2025 can be sown again. #seeds #sowing #sowingfebruary
Liked 2 times
Outside temperature - Conservatory - Me - Greenhouse has to wait for more!😩
Show 1 answer

Liked 3 times
The first harvest can slowly begin ❤️❤️❤️ Wintertime without a greenhouse
Popular Articles

Gardening in March: Preparation & Cultivation

Propagating Peppers/Chillies: How to Grow Them Successfully

Cultivation or Direct Sowing: When and Which Vegetables to Propagate?

Sowing and Propagating Tomatoes: This Is How It Works

Raised Beds: Your Planting Plan for a Year

Plant Lights for Growing and Overwintering Plants

Growing Cucumbers Seedlings in Pots: Tips for Propagation

Pricking Out Vegetable Plants: Tips and Instructions

Growing & Harvesting Rocket: Good & Bad Companion Plants

How to Grow Broccoli: Tips for Cultivation